Motorcycles come in many shapes and styles, each designed to cater to specific riding experiences and purposes. From sleek sportbikes to rugged adventure motorcycles, the diversity in two-wheeled machines reflects the wide-ranging preferences of riders around the world. But behind the polished, showroom-ready bikes lies a meticulous and innovative prototyping process that transforms conceptual ideas into reality.
Types of Motorcycles: A Ride for Every Style
1. Sportbikes
Sportbikes are designed for speed, agility, and performance. With aerodynamic bodywork, powerful engines, and aggressive riding positions, these motorcycles are ideal for thrill-seekers and track enthusiasts. Popular models include the Yamaha YZF-R1 and Kawasaki Ninja ZX-10R.
2. Cruiser Motorcycles
Cruisers prioritize comfort and style, often featuring low seats, relaxed handlebars, and a laid-back riding position. They are perfect for long-distance cruising. Harley-Davidson and Indian Motorcycles are synonymous with this category, offering iconic models like the Fat Boy and Scout.
3. Touring Motorcycles
Built for endurance, touring bikes come equipped with large fuel tanks, comfortable seating, and advanced features like GPS systems and storage compartments. They are perfect for cross-country adventures. The Honda Gold Wing and BMW K 1600 GT are well-known examples.
4. Adventure Motorcycles
Adventure bikes, or ADV bikes, are versatile machines capable of handling both on-road and off-road terrains. With robust suspension, high ground clearance, and rugged construction, models like the KTM 1290 Super Adventure and BMW GS series are built for exploration.
5. Naked Bikes
Stripped of unnecessary bodywork, naked bikes emphasize raw performance and street appeal. They are lightweight, easy to maneuver, and perfect for city riding. Examples include the Yamaha MT-09 and KTM Duke series.
6. Dirt Bikes
Designed for off-road trails, dirt bikes are lightweight and equipped with knobby tires and high suspension travel. These motorcycles are built to tackle rough terrains with ease. Popular models include the Honda CRF450R and KTM SX-F.
7. Cafe Racers
Cafe racers are retro-inspired bikes that focus on minimalism and performance. These custom-styled motorcycles often feature clip-on handlebars, single seats, and a sleek design. Triumph’s Thruxton series and Royal Enfield Continental GT 650 are classic examples.
The Role of Prototyping in Motorcycle Development
Every motorcycle begins its journey as an idea—a concept drawn from market research, technological advancements, and rider preferences. Automotive Prototyping is the critical phase where these ideas take shape, allowing designers and engineers to test their concepts before production.
1. Concept Sketches and Digital Modeling
The prototyping process begins with concept sketches and computer-aided design (CAD) models. Designers create detailed 2D and 3D representations of the motorcycle, visualizing its overall form, ergonomics, and features. Advanced CAD software allows engineers to simulate performance factors such as aerodynamics and weight distribution.
2. Clay Models and Scale Prototypes
Once the digital design is finalized, clay models or 3D-printed scale prototypes are created. These physical models help designers assess the motorcycle’s aesthetics, proportions, and ergonomic comfort. At this stage, feedback is gathered from stakeholders, and necessary adjustments are made.
3. Functional Prototypes
After the design is approved, functional prototypes are developed. These early versions of the motorcycle are built using real components, such as engines, frames, and suspension systems. Functional prototypes allow engineers to test the bike’s performance, handling, and reliability in real-world conditions. For example, sportbike prototypes undergo rigorous track testing to ensure they meet speed and agility benchmarks.
4. Material Testing and Optimization
Prototyping also involves experimenting with materials to optimize the motorcycle’s weight, durability, and performance. Adventure and dirt bikes, for instance, require lightweight yet robust materials to withstand rough terrains. This phase helps manufacturers strike the perfect balance between performance and cost.
5. Advanced Testing and Refinement
Prototypes undergo extensive testing, from wind tunnel analysis for aerodynamics to crash testing for safety. Touring motorcycles, for example, are tested for long-distance comfort and stability under varying loads. Feedback from these tests is used to refine the prototype until it meets the desired standards.
6. Final Pre-Production Model
Once all modifications are made, a final prototype, also known as the pre-production model, is created. This version is nearly identical to the production model and serves as the last checkpoint before mass manufacturing begins.
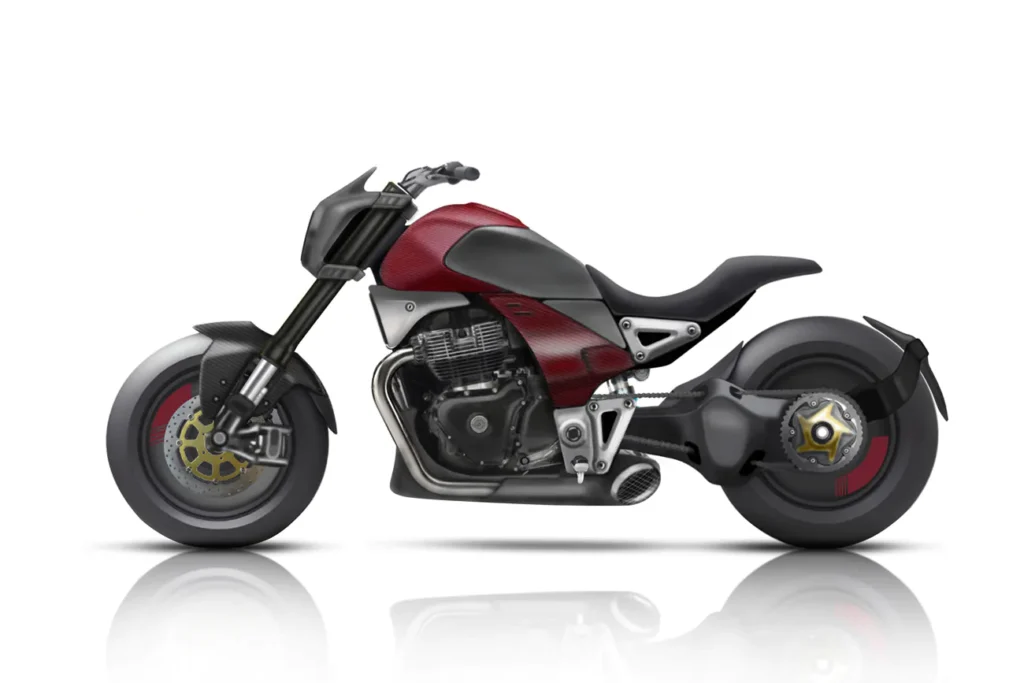

Prototyping Challenges and Innovations
Prototyping motorcycles is a complex process that involves balancing innovation, cost, and feasibility. Advanced technologies like 3D printing and virtual reality are revolutionizing the prototyping landscape, enabling faster and more accurate iterations. For example, 3D printing allows manufacturers to produce complex components in a matter of hours, significantly reducing development time.
Electric motorcycles are another area where prototyping is evolving rapidly. Designing lightweight battery packs, efficient cooling systems, and user-friendly interfaces requires cutting-edge prototyping methods. Companies like Zero Motorcycles and Harley-Davidson’s LiveWire have leveraged these innovations to bring high-performance electric bikes to market.
Conclusion
The diversity in motorcycle types reflects the varied needs and passions of riders, from adrenaline junkies seeking speed to adventurers exploring uncharted paths. Behind every motorcycle lies a meticulous prototyping process that ensures the machine not only performs as intended but also delivers an unparalleled riding experience.
Prototyping is the bridge between imagination and reality, blending art and engineering to create motorcycles that captivate and inspire. As technology continues to advance, the process will only become more efficient and innovative, shaping the future of motorcycling in exciting and unexpected ways. Whether it’s a cafe racer or an electric adventure bike, each prototype represents a vision, a challenge, and ultimately, a triumph in the world of two-wheelers.
